
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disease that causes high blood sugar. In this disease your body either doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t effectively use the insulin it makes. Insulin is a hormone produced by your pancreas. Insulin helps glucose get into your cells to be used for energy.
Glucose is your body’s main source of energy. Your body can make glucose, but glucose also comes from the food that you eat.
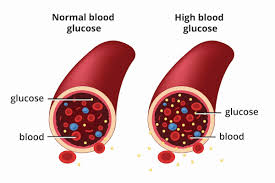
Blood sugar must be carefully regulated by insulin. Insulin’s role is to regulate the amount of glucose (sugar) in the blood. Too much blood glucose (sugar) can cause damage to organs, blood vessels, and nerves. Your body also needs insulin in order to use sugar for energy.
If you have diabetes, your body doesn’t make enough insulin, or doesn’t use insulin properly. Glucose then stays in your blood and doesn’t reach your cells.
Types of Diabetes Mellitus
There are mainly three type of Diabetes Mellitus , these are Type 1, Type 2, Gestational diabetes. and one other type of Diabetic condition that is called Pre-diabetic condition.
Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is also called insulin-dependent diabetes, it is an autoimmune disease . People with type 1 diabetes aren’t able to produce their own insulin (and can’t regulate their blood sugar) or produce in very less amount, because your immune system attacks and destroys the cells in your pancreas that make insulin.
People with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day to stay alive. or use an insulin pump to ensure their bodies have the right amount of insulin.
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is most common type of diabetic. People with type 2 diabetes, the cells in there body don’t use insulin properly. The pancreas may be making insulin but is not making enough insulin to keep your blood glucose level in the normal range. Roughly 90% – 95% of people living with diabetes have type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is most commonly developed in adulthood, although it can also occur at any age, even during in childhood. The risk factors for type 2 diabetes, such as overweight or obesity, and a family history of the disease.
Type 2 diabetes can sometimes managed with healthier lifestyle, such as healthy eating and regular exercise, losing weight or preventing weight gain, alone, but may also require medications or insulin therapy.
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is high blood sugar during pregnancy it is a temporary form of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy. Insulin-blocking hormones produced by the placenta cause this type of diabetes. Sometimes diabetes diagnosed during pregnancy is type 2 diabetes. Most of the time, this type of diabetes goes away after the baby is born.
A diagnosis of gestational diabetes may increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes diabetes later in life for both mother and child. Between 3 % to 20 % of pregnant women are affected that.
Prediabetes
Prediabetes is a condition where blood glucose (sugar) levels are higher than normal but are not high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. Although not prediabetes people will develop type 2 diabetes but many people have higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.
It’s important to know if you have prediabetes, research has shown that the you have higher risk for heart disease than people with normal glucose levels.
Why is diabetes education important for diabetic patients ?
Symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus
Some of the general symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus like type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes are –
- Increased thirsty than usual.
- Increased hunger
- Urinating often.
- Losing weight without trying.
- Presence of ketones in the urine. Ketones are a byproduct of the breakdown of muscle and fat that happens when there’s not enough available insulin.
- Feeling tired and weak.
- Feeling irritable or having other mood changes.
- Having blurry vision.
- Having slow-healing sores.
- Getting a lot of infections, such as gum, skin and vaginal infections.