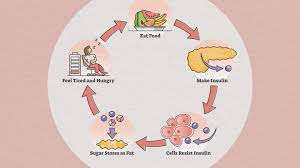
Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body’s cells become less responsive to the hormone insulin. Insulin is produced by the pancreas and plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar (glucose) levels by helping glucose enter the cells to be used for energy. When cells become resistant to insulin, glucose is less effectively transported into the cells, leading to elevated levels of glucose in the bloodstream.
Key Points About Insulin Resistance:
Causes:
- Obesity: Excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen, can increase insulin resistance(IR).
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes to the development of IR.
- Diet: High consumption of processed foods, sugary beverages, and refined carbohydrates can impact insulin sensitivity.
- Genetics: Family history can play a role in an individual’s susceptibility to IR.
- Hormonal Changes: Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can also lead to IR.
Symptoms:
- Weight gain, especially around the midsection
- Fatigue and low energy levels
- Difficulty concentrating (often referred to as “brain fog”)
- Increased hunger
- Skin changes, such as dark patches (acanthosis nigricans)
Health Risks:
If left unaddressed, it can lead to:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Heart disease
- Fatty liver disease
- Other metabolic disorders
Management and Prevention:
- Healthy Diet: Focus on whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit sugars and refined carbs.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week, such as walking, jogging, or strength training.
- Weight Loss: Losing even a small percentage of body weight can significantly improve insulin sensitivity.
- Stress Management: Techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help reduce stress, which may improve insulin response.
- Medical Consultation: Regular check-ups and monitoring blood sugar levels can help manage and identify IR early.
If you suspect you have insulin resistance, consulting with a healthcare professional is important for proper diagnosis and personalized management strategies.